Real-time Energy Monitoring
Prevent Energy Loss
Prevent Breakdowns
Preventive Maintenance
EnMonitor - Remote Energy Monitoring
EnMonitor provides end-to-end remote energy monitoring. It provides a real-time view of the energy being consumed by an organization. As a result, it highlights all the major areas of possible energy savings.
Prevent Energy Loss
Prevent Breakdowns
Understand Usage Pattern
Control Load
How it Works
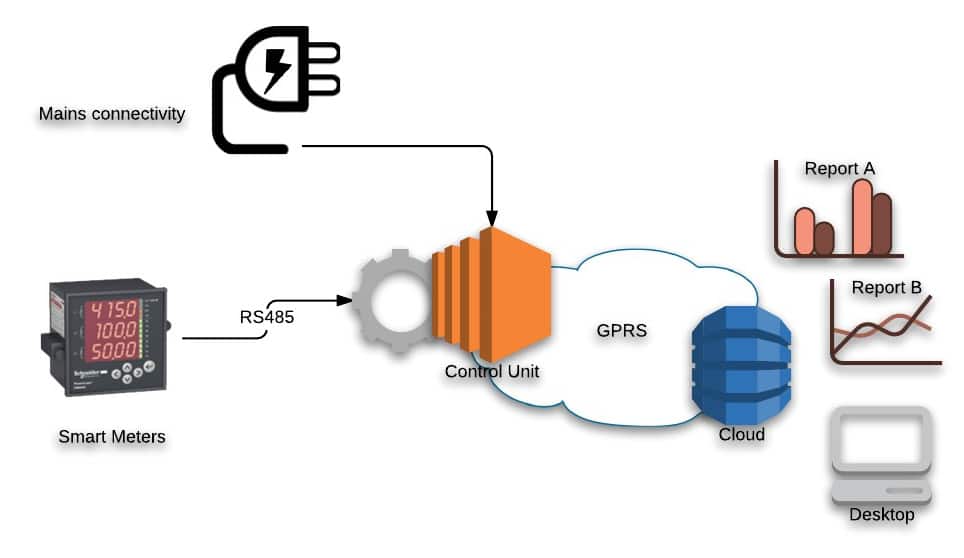
It’s an IoT (Internet of Things) based solution comprising of hardware and software components. Mainly, the hardware includes a smart meter with RS 485 connectivity and a controller. It's an industrial grade controller with GPRS connectivity. So the first step is to collect the electrical data through the smart meters. In essence, it allows the controller to capture all the key power and energy parameters. Besides, volts and amperes, it also captures parameters like power factor (PF), harmonics, demand forecast etc. This variation depends on the type of smart meter used. The controller then sends the data to the backend cloud server over GPRS. The server stores the data for years. Furthermore, it also analyses the data in real-time to notify the users of any anomalies. The user can define these notification thresholds on any of the smart meter electrical parameters. Overall, this allows the user to capture any sort of energy loss immediately and prevent a breakdown. One is able to identify specific areas of possible energy savings. On top of this, analysis of the data allows to see the energy consumption pattern over various periods. Hence, this gives complete control to the user on organisation's end-to-end energy usage and provides avenues for going green. Similarly, we have a remote fuel monitoring solution for diesel generators used in enterprises.
Benefits
eliminate manual process of noting data in books
access digital energy data anytime, anywhere
prevent breakdowns
prevent penalties due to higher consumption than contractual load
identify consumption pattern & predict demand for energy bidding
identify and explain excessive energy use
detect instances when consumption is unexpectedly higher or lower than would usually have been the case
visualize energy consumption trends (daily, weekly, seasonal, operational…)
determine future energy use and costs when planning changes in the business
diagnose specific areas of wasted energy
observe how changes to relevant driving factors impact energy efficiency
develop performance targets for energy management programs
manage energy consumption, rather than accept it as a fixed cost

Top Customers










